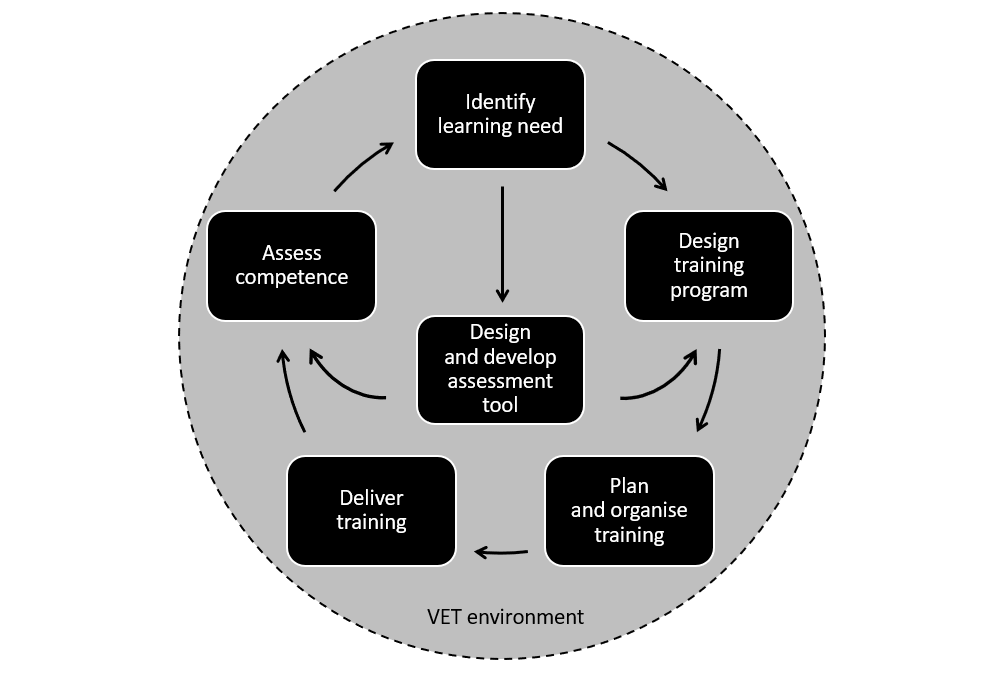
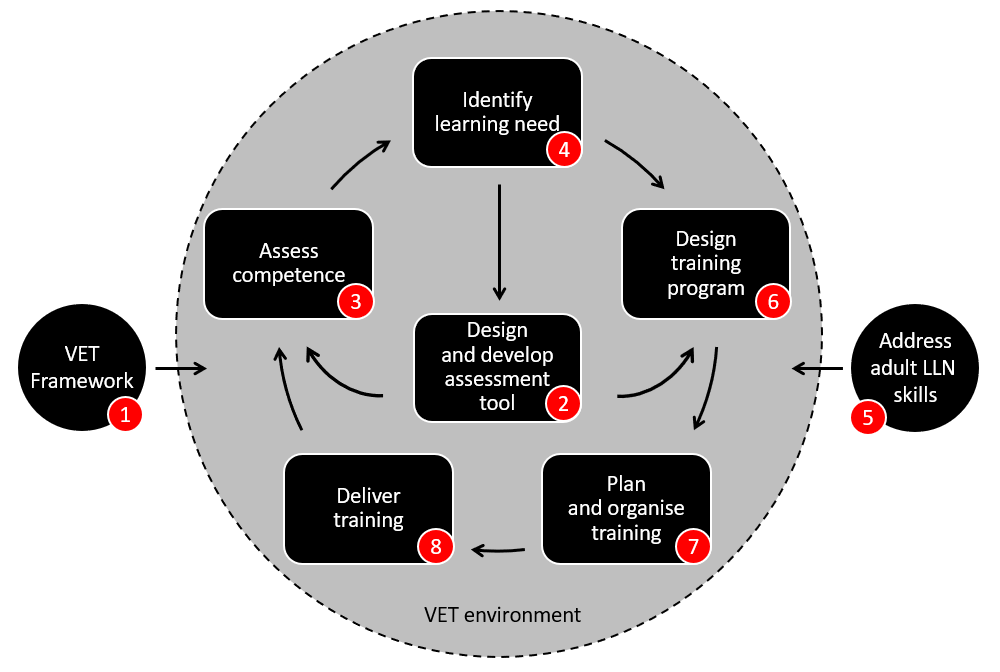
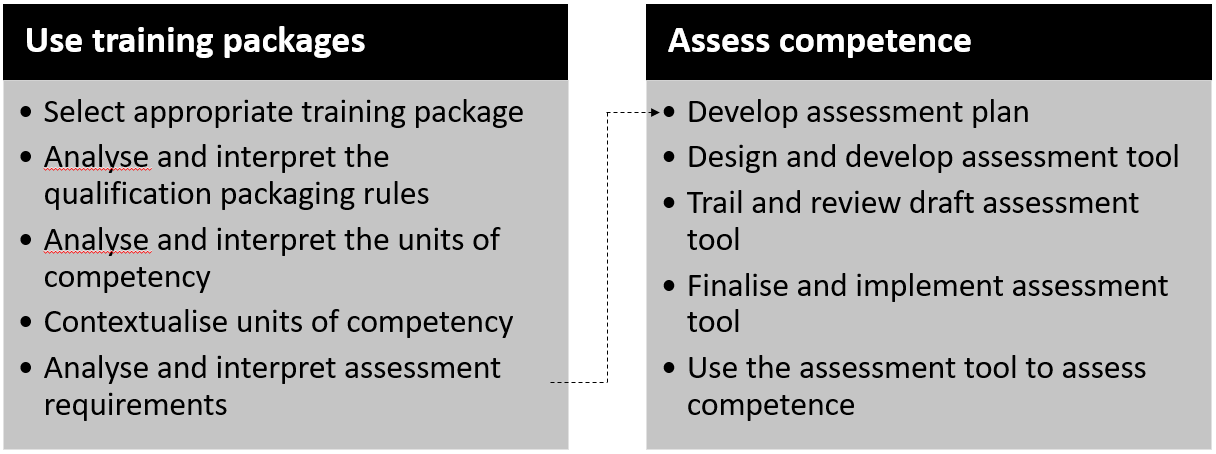
This article is primarily aimed at helping TAE Students who are studying the TAEDES402 Use training packages and accredited courses to meet client needs unit. However, it may also be of interested to recently qualified or experienced VET practitioners to refresh their ability to use training packages.
A 12-step process shall illustrate my approach to using a training package qualification to design a training program.
Step 1. Consult with client to understand their needs
For the purpose of this article I have created a scenario. This represents a synopsis of a client’s needs gathered from consultation.
Scenario
Let’s say, you work for an RTO that has been contracted by a community-based youth employment service to deliver some training. This client has been granted government funding to implement an innovative youth training and employment program.
Learners are early school leavers, typically with poor literacy skills, aged between 17 and 21.
The training program aims to prepare unemployed youth for basic office administration work. The client wants an emphasis on the development of computer skills.
A recent survey of local businesses identified that most use Microsoft Office applications.
The following photo can be considered as the type of learners expected to attend the training program.

Step 2. Select a relevant qualification
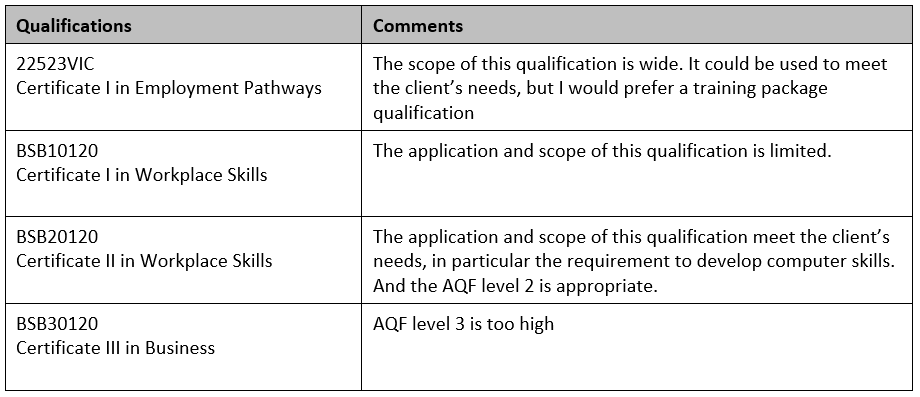
Consider option. For example:
- 22523VIC Certificate I in Employment Pathways
- BSB10120 Certificate I in Workplace Skills
- BSB20120 Certificate II in Workplace Skills
- BSB30120 Certificate III in Business
Step 3. Download qualification packaging rules

Step 4. Create table
Create a table with 4 columns. The number of rows is determined by the total number of units required plus two. For example, the BSB20120 Certificate II in Workplace Skills qualification will need a 4 x 12 table.
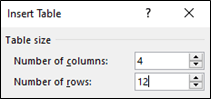
The result is the following blank table.

Step 5. Format table

Note: The table has 10 rows to insert a total of 10 units that is specified by the BSB20120 Certificate II in Workplace Skills qualification packaging rules.
Step 6. Insert core units

Step 7. Select elective unit to meet the client needs

Step 8. Check compliance with qualification packaging rules

Step 9. Give structure and sequence to the qualification

Note: Some units of competency may have prerequisites specified. A prerequisite unit must be completed first. Therefore, they have an influence on the sequence.
Step 10. Present training program to client for approval
Initially, seek agreement with the ‘big picture’.

Outline the recommended units of competency after the ‘big picture’ has been agreed to.

Step 11. Determine duration for the training program

Step 12. Draft the training and assessment strategy
For example:
BSB20120 Certificate II in Workplace Skills (Release 1)
Qualification description
This qualification reflects the role of individuals in a variety of entry-level Business Services job roles.
This qualification also reflects the role of individuals who have not yet entered the workforce, and are developing the necessary skills in preparation for work.
These individuals carry out a range of basic procedural, clerical, administrative or operational tasks that require self-management and technology skills. They perform a range of mainly routine tasks using limited practical skills and fundamental operational knowledge in a defined context. Individuals in these roles generally work under direct supervision.
Licensing/Regulatory information
No licensing, legislative or certification requirements apply to this qualification.
Entry requirements
Nil
Client needs
The client is a community-based youth employment service. They want a training program to prepare unemployed youth for basic office administration work, with an emphasis on the development of computer skills.
A recent survey of local businesses identified that most use Microsoft Office applications.
Learner characteristics
Learners are early school leavers, typically with poor literacy skills, aged between 17 and 21.
Training program structure
The training program has a structured covering four themes:
- Work safely
- Work effectively
- Work sustainably
- Use technology.
Units of competency
The qualification shall be delivered with the following ten units of competency.

Training mode and duration
The training shall be group-based learning facilitated by a trainer. The group size may be up to 20 learners.
There is a total duration of 25 training days. Each day shall be consistent with ‘normal’ business hours:
- 9:00am start time
- 5:00pm finish time
The training program shall be delivered over a period of five weeks.
Training delivery schedule
The following is the delivery schedule for the entire training program.
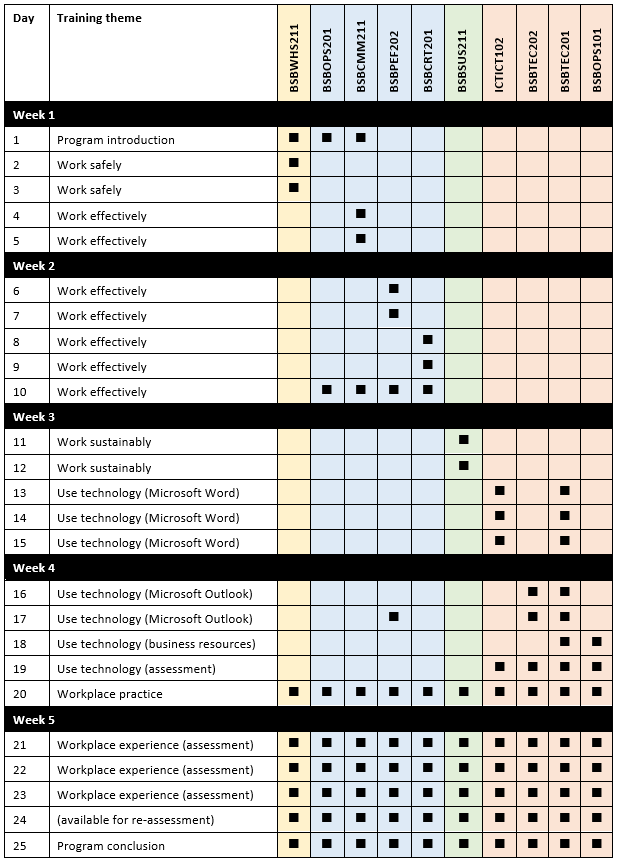
Assessment approach
Evidence of competency shall be gather using a range of assessment methods.
- Questioning (Q)
- Observation of performance (OP)
- Review of products (RP)
- Third-party reports. (TPR)
Refer to assessment tools for details.
The following is an overview of the assessment schedule.

Note: Opportunities for re-assessment shall be arranged.
In conclusion
The above draft training and assessment strategy is incomplete. However, for the purpose of this article, it gives a clear example about how a training program can be designed to meet a client’s need.
- Do you find the 12-step process a useful guide?
- Did you learn something from this article?
Australia’s VET system
Australia’s vocational education and training (VET) system is complex and forever changing. People studying for their TAE40122 Certificate IV in Training and Assessment qualification may find useful information on this website. Tap or click on the following ABC logo to find out more.

Training trainers since 1986