
The TAEASS412 Assess competence unit of competency over-complicates the process of assessing competency. This unit has 6 elements, 31 performance criteria, and 11 foundations skills that are assessable. And many of the performance criteria have been stuffed with details.
This article unpacks the TAEASS412 Assess competence unit of competency, and give a plain and simple explanation of how to conduct competency-based assessment.
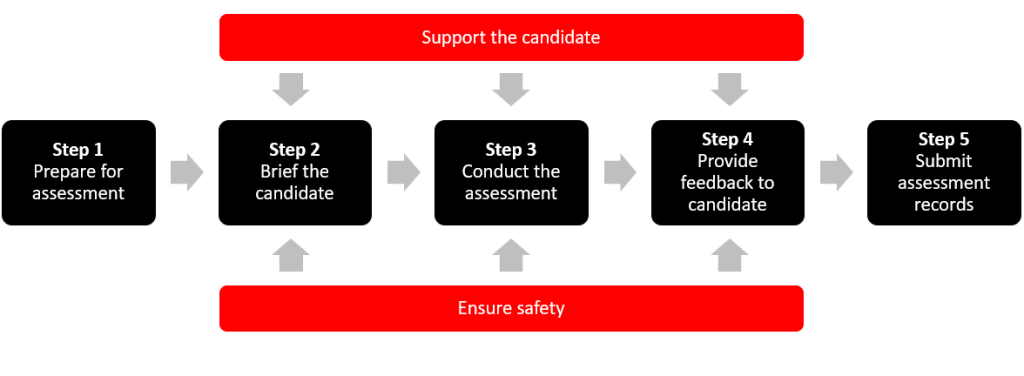
There are five keys steps to assessing competence:
- Step 1. Prepare for assessment
- Step 2. Brief the candidate
- Step 3. Conduct the assessment
- Step 4. Provide feedback to candidate
- Step 5. Submit assessment records.
Step 1. Prepare for assessment

In theory, information about how the assessment is to be conducted will be in the assessment tool. An assessor should read the assessment tool and identify the following:
- assessment methods and assessment instruments to be used
- where and when the assessment tasks will be conducted
- actions to be undertaken by candidate and assessor in preparation for assessment
- facilities, equipment and resources required.
Facilities, equipment and resources required for the assessment may need to be organised or booked in advance.
Step 2. Brief the candidate

The assessor should conduct an assessment briefing to ensure that the candidate is fully aware about:
- assessment process and opportunities for re-assessment
- standard of performance required to be assessed as competent
- where and when the assessment tasks will be conducted
- actions to be taken in preparation for assessment
- equipment, resources or PPE required
- safety precautions, if applicable.
This is the time to confirm that the candidate understands the assessment process and is aware of their right to appeal. It is a good idea to check that the candidate is ready to be assessed.
Step 3. Conduct the assessment

The assessor must ensure that the assessment is conducted according to principles of assessment and rules of evidence. And the assessor must ensure that assessment is conducted safely.
The assessor shall use the assessment instruments from the assessment tool to gather evidence and record their assessment decisions. The assessment decisions must be based on the evidence gathered.
Step 4. Provide feedback to candidate

Provide the candidate with feedback about the assessment outcome and the standard achieved. If required, inform the candidate about the need for re-assessment including what needs to be re-assessed, where the re-assessment will be done, and when it need to be done by.
Step 5. Submit assessment records

The assessor shall complete and submit assessment records and results. Assessment records and results must be kept confidential.
Support and safety
Two of the responsibilities that an assessor has when conducting assessments are:
- Support the candidate
- Ensure safety.
The following diagram shows the relationship between these two responsibilities and the five keys steps to assessing competence
Support the candidate
The assessor should discuss availability of support when conducting the assessment briefing. The assessor should monitor the candidates progress and determine if any support is needed. And the assessor needs to be available to provide or organise support should it be needed.
Ensure safety
Two types of safety should be considered:
- Physical safety
- Emotional safety.
It is a good idea to conduct a risk assessment focused on safety before conducting the assessment. Risks may include:
- Safety issues relating to the assessment environment
- Safety issues relating to the work tasks being performed and assessed
- The emotional safety and wellbeing of the candidate.
The assessor must monitor safety throughout the assessment process, and stop the assessment process if there is a potential or actual safety issue.
RTO assessment system
Assessments are conducted within an RTO’s assessment system.
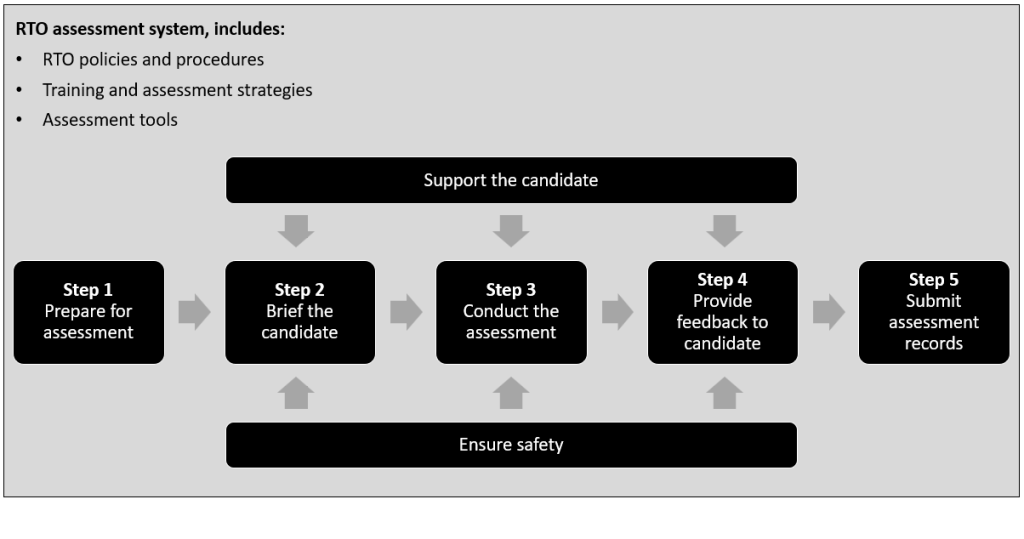
The assessor shall need to read and understand the following documents:
- RTO policies and procedures
- Training and assessment strategy (TAS)
- Assessment tool.
The RTO policies and procedures may include:
- Safety
- Support arrangements
- Record keeping
- Privacy and confidentiality
- Reasonable adjustment
- Appeals and complaints
- Assessment review
- Assessment validation.
The training and assessment strategy (TAS) should provide an overview about how the assessment is to be conducted. The scope of this document will be a qualification, skill set or stand-alone unit. Examples of units that are delivered as stand-alone include:
- First aid
- Food safety
- Construction induction
- Responsible service of alcohol.
The assessment tool should provide the details about how the assessment is to be conducted. The assessment can be for a unit or cluster of units. The assessor must read and understand the assessment tool as a first step to prepare for the assessment. Then, the assessment tool should be used to guide the assessment process. And the assessment instruments are to be used to record gathered evidence and results.
In conclusion
The aim of this article has been to give a plan and simple explanation about how to conduct competency-based assessment. Some TAE Students may be presented with a much more complicated explanation about how to assess competence. If it begins to seem complex or difficult to understand, it would be worth remembering these five steps:
- Step 1. Prepare for assessment
- Step 2. Brief the candidate
- Step 3. Conduct the assessment
- Step 4. Provide feedback to candidate
- Step 5. Submit assessment records.
Do you need help with your TAE studies?
Are you a doing the TAE40122 Certificate IV in Training and Assessment, and are you struggling with your studies? Do you want help with your TAE studies?

Ring Alan Maguire on 0493 065 396 to discuss.

Training trainers since 1986
